Navigating Wealth Growth with ETF Savings Plans
- FIO Legal Solutions
- Apr 4, 2024
- 3 min read

Exchange-Trade Fund (ETF) savings plans have emerged as a powerful tool for both novice and seasoned investors aiming to diversify their portfolio and grow their wealth efficiently. Unlike traditional savings methods, ETF savings plans offer a blend of accessibility, flexibility, and affordability, making them an increasingly popular choice for long-term financial planning.
How ETF Savings Plans Work
ETF savings plans enable investors to pool funds into a diversified portfolio of assets, including stocks, bonds, cryptocurrencies, and commodities, all within a single investment vehicle that trades on stock exchanges. This approach not only simplifies the investment process but also provides the liquidity and flexibility not typically found in mutual funds, due to the ability to trade ETF shares throughout the trading day at market prices.
The structure of ETFs also offers tax efficiency by minimizing capital gains distributions, an attractive feature for those looking to maximize long-term gains. With the vast array of ETFs available, investors can tailor their investment strategy to align with personal goals and risk tolerance, whether that involves focusing on specific sectors, themes, or broad market indices.
Investment Strategies with ETF Savings Plans
Adopting an ETF savings plan can significantly contribute to achieving long-term financial goals like retirement. The key advantage lies in the ability to access diverse asset classes and geographic regions through a single investment, thereby spreading risk and enhancing portfolio stability over time. By setting up automatic contributions to selected ETFs, investors can cultivate a disciplined approach to saving, essential for navigating market fluctuations and building wealth gradually.
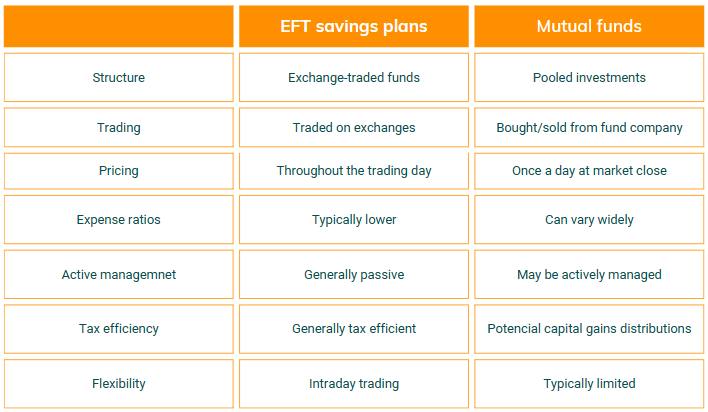
ETF Savings vs. Traditional Savings and Mutual Funds
Comparing ETF savings plans to traditional savings accounts or mutual funds highlights their potential for higher returns, given the typically lower interest rates associated with bank savings. ETFs offer more investment flexibility and tax advantages, presenting a customizable solution to meet individual financial objectives and risk profiles.
While mutual funds may provide active management and potentially lower trading costs for frequent transactions, ETFs generally boast lower expense ratios and greater tax efficiency. This makes ETFs a compelling option for those seeking a balance between risk and flexibility in their investment strategy.
ETF Savings vs. Traditional Savings
Benefits and Considerations of ETF Savings Plans
ETF savings plans stand out for their capacity to offer instant diversification, lower overall costs compared to actively managed funds, and the liquidity to trade at market prices throughout the day. These features, combined with the broad selection of ETFs covering various asset classes and investment strategies, allow investors to tailor their portfolios to their specific financial goals and risk tolerance.
ETF Savings vs. mutual funds
However, potential investors should be aware of risks and considerations, such as market volatility, liquidity risks, management fees, tracking errors, and concentration risks. Understanding these factors is crucial for effectively managing an ETF savings portfolio and making informed investment decisions.
Conclusion
ETF savings plans represent a strategic option for investors seeking a diversified, affordable, and flexible way to build wealth over time. By offering a straightforward path to investing in a wide range of asset classes and providing tax efficiencies and lower expense ratios, ETFs can play a critical role in long-term financial planning and retirement strategies.
As with any investment, understanding the associated risks and maintaining a disciplined approach to saving and investing is key to capitalizing on the benefits ETF savings plans have to offer.
Navigating the risks associated with ETF savings plans requires a clear understanding of the potential challenges investors may face.
Market volatility is a significant factor, as the value of ETF shares can fluctuate widely in response to changes in the underlying assets, impacting investment returns.
Liquidity risk also plays a role, particularly during periods of market stress when trading volumes can drop, potentially making it difficult to buy or sell shares at desired prices.
Although ETFs typically offer lower expense ratios than actively managed funds, investors must still account for management fees and other costs associated with trading. Tracking error is another concern, where an ETF may fail to precisely replicate the performance of its benchmark index due to factors like sampling techniques, trading expenses, and fees.
Concentration risk can arise if an ETF is heavily weighted towards a specific sector or asset class, increasing vulnerability to sector-specific downturns.
Lastly, understanding the tax implications of ETF investments is crucial, as certain transactions within ETFs can trigger taxable events.
Careful consideration of these risks is essential for investors aiming to effectively manage their ETF savings portfolios and achieve their financial goals.
#FinancialPlanning #ETFInvesting #SavingsPlans #InvestmentStrategies #ETFs #InvestmentPlanning #ETFPortfolio #FinancialLiteracy #ETFsavings #SmartInvesting